Development of a novel MR clutch featuring tooth-shaped disc
Author affiliations
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15625/0866-7136/15879Keywords:
magnetorheological fluid (MRF), MR clutch, tooth-shaped rotor, optimal designAbstract
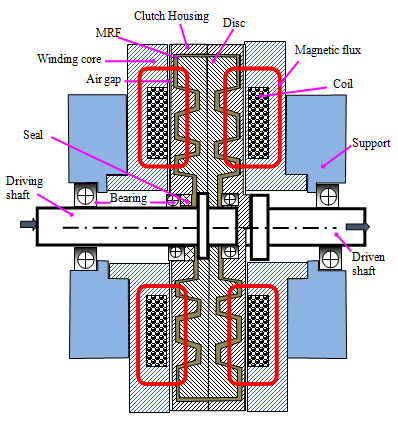
In this research, we focus on development of a new configuration of magneto-rheological fluid (MRF) based clutch (MRC) featuring a tooth-shaped disc with multiple teeth acting as multiple magnetic poles of the clutch. The tooth-shaped disc is placed in a clutch housing composed of the left housing and the right housing. The inner face the housing also has tooth shaped features mating with the teeth of the disc through the working MRF. Excitation coils are placed directly on stationary winding cores placed on both side of the clutch housing. An air gap of 0.3 mm is left between the housing and the winding cores to ensure the housing can freely rotate against the winding cores. After the introductory part, configuration of the MRC is introduced and the transmitted torque of the MRC is derived. An optimization process to minimize the overall volume of the proposed clutch, which can generate a required maximum braking torque, is then conducted. The optimal results show that the overall volume of the proposed MRC is significantly reduced compared to a referenced conventional MRC (0.159 m3 vs. 0.295 m3). A prototype of the proposed MRC is fabricated for experimental works and good agreement between the experimental results and simulated ones is archived.
Downloads
References
J. Wang and G. Meng. Magnetorheological fluid devices: Principles, characteristics and applications in mechanical engineering. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part L: Journal of Materials: Design and Applications, 215, (2001), pp. 165–174.
A. Muhammad, X. liang Yao, and Z. chao Deng. Review of magnetorheological (MR) fluids and its applications in vibration control. Journal of Marine Science and Application, 5, (2006), pp. 17–29.
T. D. Truong, V. Q. Nguyen, B. T. Diep, D. H. Q. Le, D. T. Le, and Q. H. Nguyen. Speed control of rotary shaft at different loading torque using MR clutch. In A. Erturk, (ed.), Active and Passive Smart Structures and Integrated Systems XIII, SPIE, (2019).
U. Lee, D. Kim, N. Hur, and D. Jeon. Design Analysis and Experimental Evaluation of an MR Fluid Clutch. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 10, (1999), pp. 701–707.
T. Kikuchi, K. Ikeda, K. Otsuki, T. Kakehashi, and J. Furusho. Compact MR fluid clutch device for human-friendly actuator. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 149, (2009).
D.Wang and Y. Hou. Design and experimental evaluation of a multidisk magnetorheological fluid actuator. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 24, (2012), pp. 640–650.
K. H. Latha, P. U. Sri, and N. Seetharamaiah. Design and Manufacturing Aspects of Magnetorheological Fluid (MRF) Clutch. Materials Today: Proceedings, 4, (2), (2017), pp. 1525–1534.
Q. H. Nguyen and S.-B. Choi. A new method for speed control of a DC motor using magnetorheological clutch. In Active and Passive Smart Structures and Integrated Systems 2014, International Society for Optics and Photonics, (2014).
Q. H. Nguyen, N. D. Nguyen, and S. B. Choi. Design and evaluation of a novel magnetorheological brake with coils placed on the side housings. Smart Materials and Structures, 24, (2015).
N. D. Nguyen, T. Le-Duc, L. D. Hiep, and Q. H. Nguyen. Development of a new magnetorheological fluid–based brake with multiple coils placed on the side housings. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 30, (2018), pp. 734–748.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Funding data
-
National Foundation for Science and Technology Development
Grant numbers 107.01-2018.335









