Multiphase topology optimization for the design of porous metamaterials with local volume constraint
Author affiliations
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15625/0866-7136/23362Keywords:
partition-of-unity mapping, multi-material topology optimization, periodic metamaterials, local volume constraintAbstract
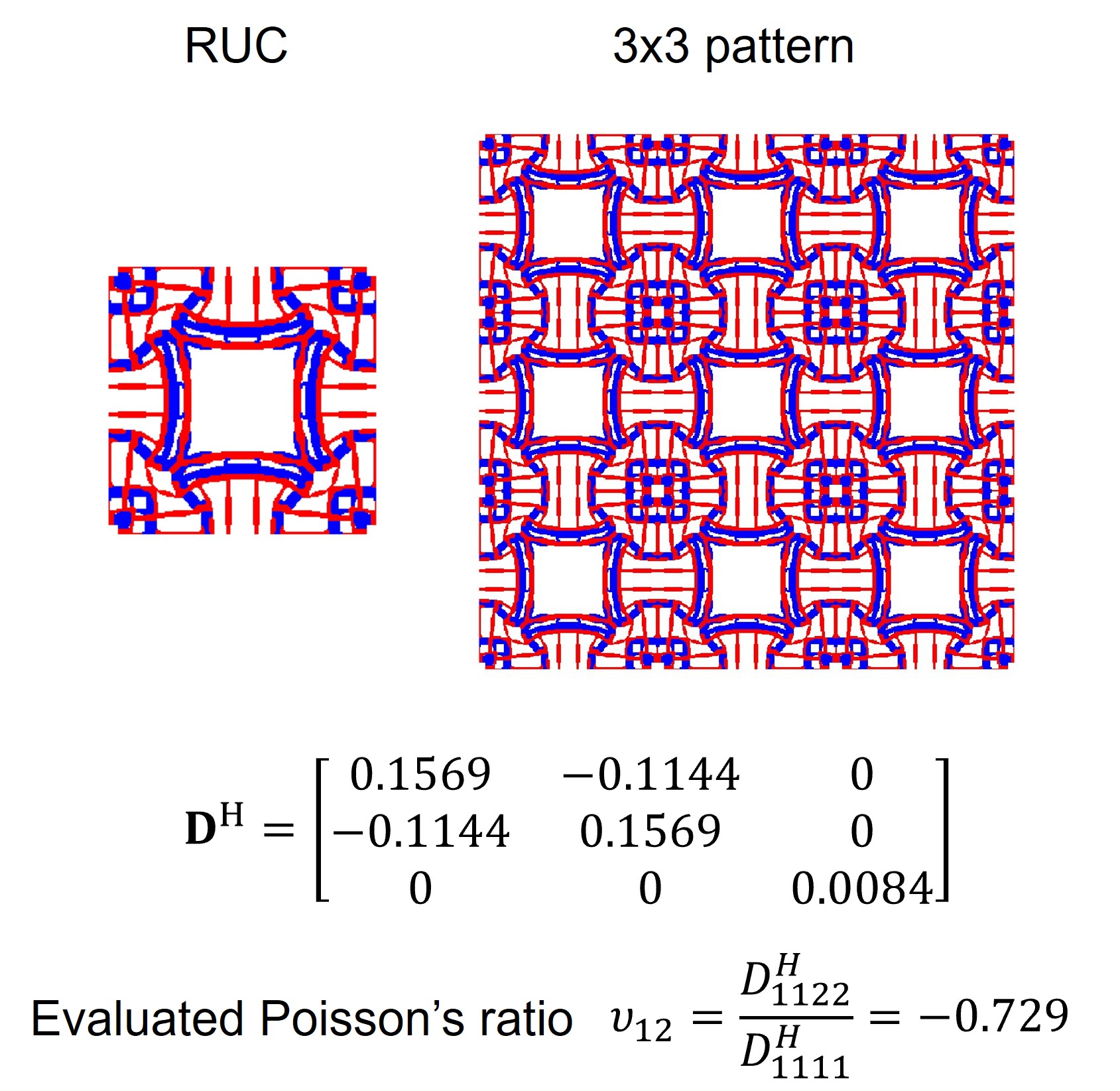
This paper presents a novel multiphase approach for topological design of porous metamaterials. Firstly, a new interpolation scheme based on partition-of-unity mapping is proposed. The scheme is employed into the design of periodic metamaterials with specified expectation on effective properties. Due to the periodicity, the design domain is defined in a Representative Unit Cell (RUC) - which represents the repeated pattern - such that the effective (or homogenized) elastic tensor is evaluated by the Strain Energy Method (SEM). In order to reduce the computational effort, the pattern is assumed to be symmetric, which is equivalent to finding metamaterials with orthotropic behavior. The allowed amount of each material is given via upper bound constraints on global volume fraction. The pore size is further controlled by requiring local volume constraint on each material phase. Via several numerical examples, which differ from each other in terms of objective function and the amount of each material phase, the feasibility of the proposed approach is demonstrated.
Downloads
References
[1] E. Andreassen and C. S. Andreasen. How to determine composite material properties using numerical homogenization. Computational Materials Science, 83, (2014), pp. 488–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2013.09.006.
[2] L. Xia and P. Breitkopf. Design of materials using topology optimization and energy-based homogenization approach in Matlab. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 52, (2015), pp. 1229–1241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-015-1294-0.
[3] W. Zhang, G. Dai, F. Wang, S. Sun, and H. Bassir. Using strain energy-based prediction of effective elastic properties in topology optimization of material microstructures. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 23, (2007), pp. 77–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-006-0045-2.
[4] M. Collet, L. Noël, M. Bruggi, and P. Duysinx. Topology optimization for microstructural design under stress constraints. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 58, (2018), pp. 2677–2695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-018-2045-9.
[5] A. Gupta, A. Gupta, and R. Chowdhury. Computational design of auxetic microstructures via stress-based topology optimization. Engineering Structures, 319, (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2024.118807.
[6] Y. Wang, J. Gao, Z. Luo, T. Brown, and N. Zhang. Level-set topology optimization for multimaterial and multifunctional mechanical metamaterials. Engineering Optimization, 49, (2016), pp. 22–42. https://doi.org/10.1080/0305215x.2016.1164853.
[7] P. Vogiatzis, S. Chen, X. Wang, T. Li, and L. Wang. Topology optimization of multi-material negative Poisson’s ratio metamaterials using a reconciled level set method. Computer-Aided Design, 83, (2017), pp. 15–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cad.2016.09.009.
[8] Z. Han and K. Wei. Multi-material topology optimization and additive manufacturing for metamaterials incorporating double negative indexes of Poisson’s ratio and thermal expansion. Additive Manufacturing, 54, (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2022.102742.
[9] J. Wu, N. Aage, R. Westermann, and O. Sigmund. Infill optimization for additive manufacturing—approaching bone-like porous structures. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 24, (2018), pp. 1127–1140. https://doi.org/10.1109/tvcg.2017.2655523.
[10] E. Fernández, M. Collet, P. Alarcón, S. Bauduin, and P. Duysinx. An aggregation strategy of maximum size constraints in density-based topology optimization. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 60, (2019), pp. 2113–2130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02313-8.
[11] S. Das and A. Sutradhar. Multi-physics topology optimization of functionally graded controllable porous structures: Application to heat dissipating problems. Materials & Design, 193, (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.108775.
[12] J. Wang, J. Wu, and R. Westermann. Stress topology analysis for porous infill optimization. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 65, (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-022-03186-0.
[13] M. Zhou, Y. Lu, Y. Liu, and Z. Lin. Concurrent topology optimization of shells with self-supporting infills for additive manufacturing. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 390, (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2021.114430.
[14] J. A. Postigo, A. Garaigordobil, R. Ansola, and J. Canales. Topology optimization of Shell–Infill structures with enhanced edge-detection and coating thickness control. Advances in Engineering Software, 189, (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2023.103587.
[15] D. Han, X. Ren, Y. Zhang, X. Yu Zhang, X. Gang Zhang, C. Luo, and Y. Min Xie. Lightweight auxetic metamaterials: Design and characteristic study. Composite Structures, 293, (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.115706.
[16] B. Yi, G. H. Yoon, R. Zheng, L. Liu, D. Li, and X. Peng. A unified material interpolation for topology optimization of multi-materials. Computers & Structures, 282, (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruc.2023.107041.
[17] O. Sigmund. A 99 line topology optimization code written in Matlab. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 21, (2001), pp. 120–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001580050176.
[18] E. Andreassen, A. Clausen, M. Schevenels, B. S. Lazarov, and O. Sigmund. Efficient topology optimization in MATLAB using 88 lines of code. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 43, (2010), pp. 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-010-0594-7.
[19] H. Liu, D. Yang, P. Hao, and X. Zhu. Isogeometric analysis based topology optimization design with global stress constraint. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 342, (2018), pp. 625–652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2018.08.013.
[20] S. Xu, J. Liu, B. Zou, Q. Li, and Y. Ma. Stress constrained multi-material topology optimization with the ordered SIMP method. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 373, (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2020.113453.
[21] K. Svanberg. The method of moving asymptotes—a new method for structural optimization. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 24, (1987), pp. 359–373. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.1620240207.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Funding data
-
National Foundation for Science and Technology Development
Grant numbers 107.02-2023.100









