Effect of heat treatment on mechanical properties of type-304 austenitic stainless steel
Author affiliations
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15625/0866-7136/22777Keywords:
austenitic stainless steel, cryogenic, heat treatment, mechanical properties, microstructureAbstract
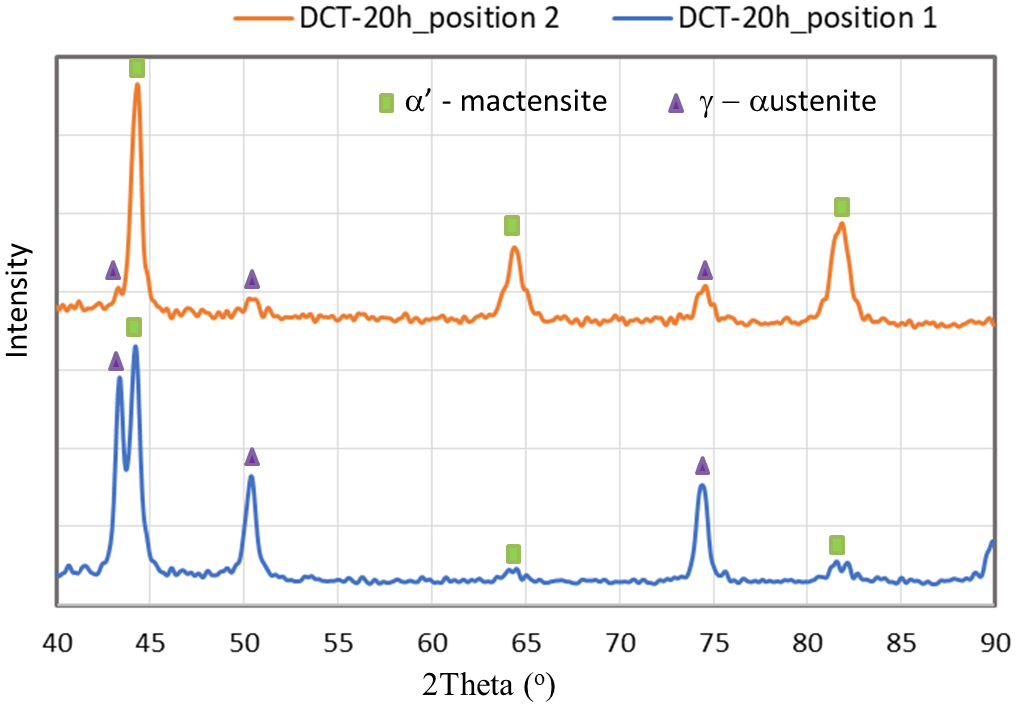
In this study, the effects of cryogenic treatment and heat treatment on the microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of type-304 austenitic stainless steel are investigated. Cryogenic treatment is conducted in a liquid nitrogen environment at -196°C, both with and without a quenching process. The experimental results indicate that traditional heat treatment processes do not lead to improvements in hardness or phase transformation. Although a modest increase in the ultimate tensile strength is observed with prolonged immersion in liquid nitrogen, deep cryogenic treatment does not produce a significant enhancement in the tensile properties of the examined material. Among the cases examined, water-quenched heat treatment without cryogenic treatment demonstrates a considerable increase in ductility. Additionally, significant differences in microstructure and hardness are observed at different locations of the tensile specimen due to martensitic transformation from the austenitic phase during plastic deformation. Consequently, improvement in the mechanical properties of the steel is not a result of the heat treatment process; rather, the heat treatment affects the stability of the austenitic phase, thereby influencing the potential for martensitic transformation during plastic deformation.
Downloads
References
[1] A. Anitha, B. Tanya, C. Bandhavi, and S. Ram. Investigation of microstructure and mechanical properties of austenite stainless steel 304 during tempering and cryogenic heat treatment. E3S Web Conferences, 84, (1), (2020). https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202018401006.
[2] N. R. Baddoo. Stainless steel in construction: A review of research, application, challenges and opportunites. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 64, (2008), pp. 1199–1206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2008.07.011.
[3] H. T. Pham and T. Iwamoto. An experimental investigation on rate sensitivity of fracture-mechanical characteristics in 304 austenitic stainless steel under bending deformation. ISIJ International, 55, (2015), pp. 2661–2666. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2015-397.
[4] J. A. Rodríguez-Martínez, A. Rusinek, and R. Pesci. Experimental survey on the behavior of AISI 304 steel sheets subjected to perforation. Thin-Walled Structures, 48, (2010), pp. 966–978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2010.07.005.
[5] H. T. Pham and T. Iwamoto. An evaluation of fracture properties of type-304 austenitic stainless steel at high deformation rate using the small punch test. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 144, (2018), pp. 249–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2018.05.056.
[6] S. Allain, J.-P. Chateau-Cornu, O. Bouaziz, S. Migot, and N. Guelton. Correlations between the calculated stacking fault energy and the plasticity mechanisms in Fe-Mn-C alloys. Materials Science and Engineering A, 387–389, (2004), pp. 158–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2004.01.059.
[7] P. L. Sun, Y. H. Zhao, J. C. Cooley, M. E. Kassner, Z. Horita, T. G. Langdon, E. J. Lavernia, and Y. T. Zhu. Effect of stacking fault energy on strength and ductility of nanostructured alloys: an evaluation with minimum solution hardening. Materials Science and Engineering A, 525, (1–2), (2009), pp. 83–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2009.06.030.
[8] A. Weiß, H. Gutte, and J. Mola. Contributions of ε and α′TRIP effects to the strength and ductility of AISI 304 (X5CrNi18-10) austenitic stainless steel. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 47, (2016), pp. 112–122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2726-y.
[9] H. T. Pham, T. Y. Doan, and T. H. N. Nguyen. A study on effect of heat treatment on straininduced martensitic transformation in type-304 austenitic stainless steel. In B. T. Long, H. S. Kim, K. Ishizaki, N. D. Toan, I. A. Parinov, and Y. H. Kim, editors, Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Mechanical Engineering, Automation, and Sustainable Development 2021 (AMAS2021), Springer, (2021), pp. 584–591. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-99666-6_84.
[10] N. B. Fredj and H. Sidhom. Effects of the cryogenic cooling on the fatigue strength of the AISI 304 stainless steel ground components. Cryogenics, 46, (6), (2006), pp. 439–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cryogenics.2006.01.015.
[11] N. B. Dhokey, S. S. Maske, and P. Ghosh. Effect of tempering and cryogenic treatment on wear and mechanical properties of hot work tool steel (H13). Materials Today, 43, (5), (2021), pp. 3006–3013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.01.361.
[12] K. J. Lee, M. S. Chun, M. H. Kim, and J. M. Lee. A new constitutive model of austenitic stainless steel for cryogenic applications. Computational Materials Science, 46, (4), (2009), pp. 1152– 1162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2009.06.003.
[13] T. H. Lee, E. Shin, C. S. Oh, H. Y. Ha, and S. J. Kim. Correlation between stacking fault energy and deformation microstructure in high-interstitial-alloyed austenitic steels. Acta Materialia, 58, (2010), pp. 3173–3186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2010.01.056.
[14] J. Shi, L. Hou, J. Zuo, L. Zhuang, and J. Zhang. Effect of cryogenic rolling and annealing on the microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of 304 stainless steel. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 24, (2017), pp. 638–645. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-017-1446-x.
[15] C. Zheng, C. Liu, M. Ren, H. Jiang, and L. Li. Microstructure and mechanical behavior of an AISI 304 austenitic stainless steel prepared by cold- or cryogenic-rolling and annealing. Materials Science and Engineering A, 724, (2018), pp. 260–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.03.105.
[16] Q. Lu, J. Zheng, G. Huang, K. Li, H. Ding, Z. Wang, and S. Cheng. Enhancing combined cryogenic mechanical properties of metastable austenitic stainless steel by warm forming. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 291, (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2020.117017.
[17] P. Jovičević-Klug, N. Lipovšek, M. Jovičević-Klug, M. Mrak, J. Ekar, B. Ambrožič, G. Dražic̈, J. Kovač, and B. Podgornik. Assessment of deep cryogenic heat-treatment impact on the microstructure and surface chemistry of austenitic stainless steel. Surfaces and Interfaces, 35, (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2022.102456.
[18] C. Wang, X. Lin, L. Wang, S. Zhang, and W. Huang. Cryogenic mechanical properties of 316L stainless steel fabricated by selective laser melting. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 815, (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2021.141317.
[19] S. Wu, J. Xin, W. Xie, H. Zhang, and C. Huang. Mechanical properties and microstructure evolution of cryogenic pre-strained 316LN stainless steel. Cryogenics, 121, (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cryogenics.2021.103388.
[20] Y. Wei, Q. Lu, Z. Kou, T. Feng, and Q. Lai. Microstructure and strain hardening behavior of the transformable 316L stainless steel processed by cryogenic pre-deformation. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 862, (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2022.144424.
[21] D. Kaoumi and J. Liu. Deformation induced martensitic transformation in 304 austenitic stainless steel: In-situ vs. ex-situ transmission electron microscopy characterization. Materials Science and Engineering A, 715, (2018), pp. 73–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.12.036.
[22] A. Jain and A. Varshney. Effect of grain size and dislocation density on the work hardening behavior of SS 304. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 34, (2025), pp. 3008–3025. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-024-09358-x.
[23] H. T. Pham and T. Iwamoto. A computational investigation on bending deformation behavior at various deflection rates for enhancement of absorbable energy in TRIP steel. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 47, (2016), pp. 3897–3911. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3565-9.
[24] B. Rafiei, B. M. Sadeghi, and B. Mirzakhani. Transformation-induced plasticity in 304 and 304L stainless steels and its effect on tensile behavior and anisotropy. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 34, (2025), pp. 5115–5125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-024-09478-4.
[25] C. Meichuan, T. Daisuke, S. Akinobu, and T. Nobuhiro. Identical area observations of deformation-induced martensitic transformation in SUS304 austenitic stainless steel. Materials Transactions, 54, (2013), pp. 308–313. https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.MBW201212.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.









